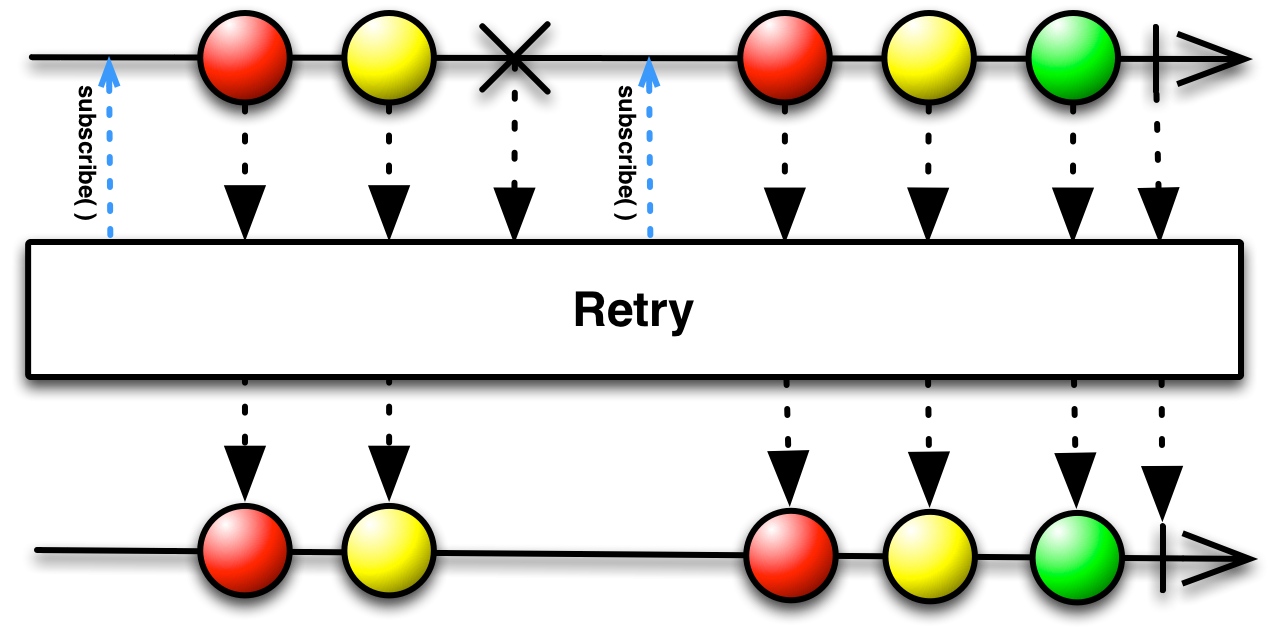
The Retry operator responds to an onError
notification from the source Observable by not passing that call through to its observers, but
instead by resubscribing to the source Observable and giving it another opportunity to complete
its sequence without error. Retry always passes
onNext notifications through to its observers, even from sequences that terminate
with an error, so this can cause duplicate emissions (as shown in the diagram above).
RxClojure does not implement the Retry operator.
RxCpp implements this operator as retry:
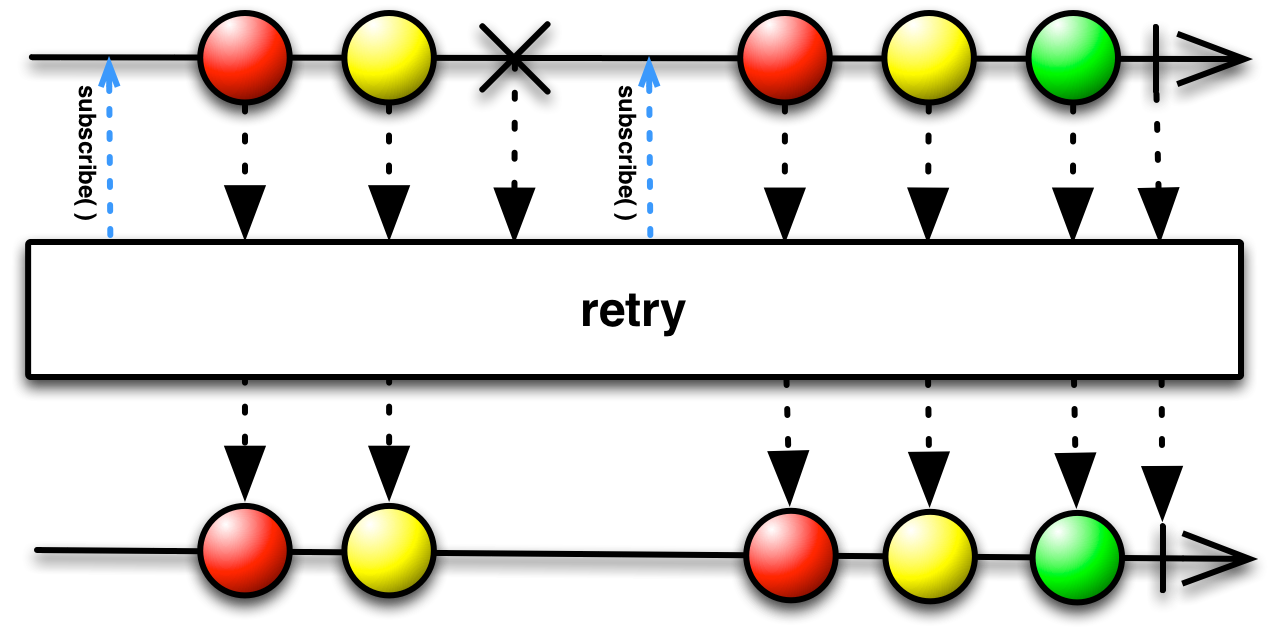
retry takes a single argument, a count of the number of times it should try
resubscribing to the source Observable when it encounters errors. If this count is exceeded,
retry will not attempt to resubscribe and will instead pass the
onError notification to its observers.
RxGroovy has two versions of this operator: retry and retryWhen.

One variant of retry takes no parameters. It will continue to resubscribe to and
mirror the source Observable no matter how many onError notifications it
receives.
Another variant of retry takes a single parameter: a count of the number of
times it should try to resubscribe to the source Observable when it encounters errors. If
this count is exceeded, retry will not attempt to resubscribe again and will
instead pass the latest onError notification to its observers.
A third variant of retry takes a predicate function as a parameter. You write
this function to accept two arguments: an Integer count of how many retries have taken place
thusfar, and a Throwable indicating the error that caused the onError
notification. This function returns a Boolean to indicate whether or not retry
should resubscribe to and mirror the source Observable. If it does not, then
retry passes the latest onError notification to its observers.
retry by default operates on the trampoline
Scheduler.
retry()retry(long)retry(Func2)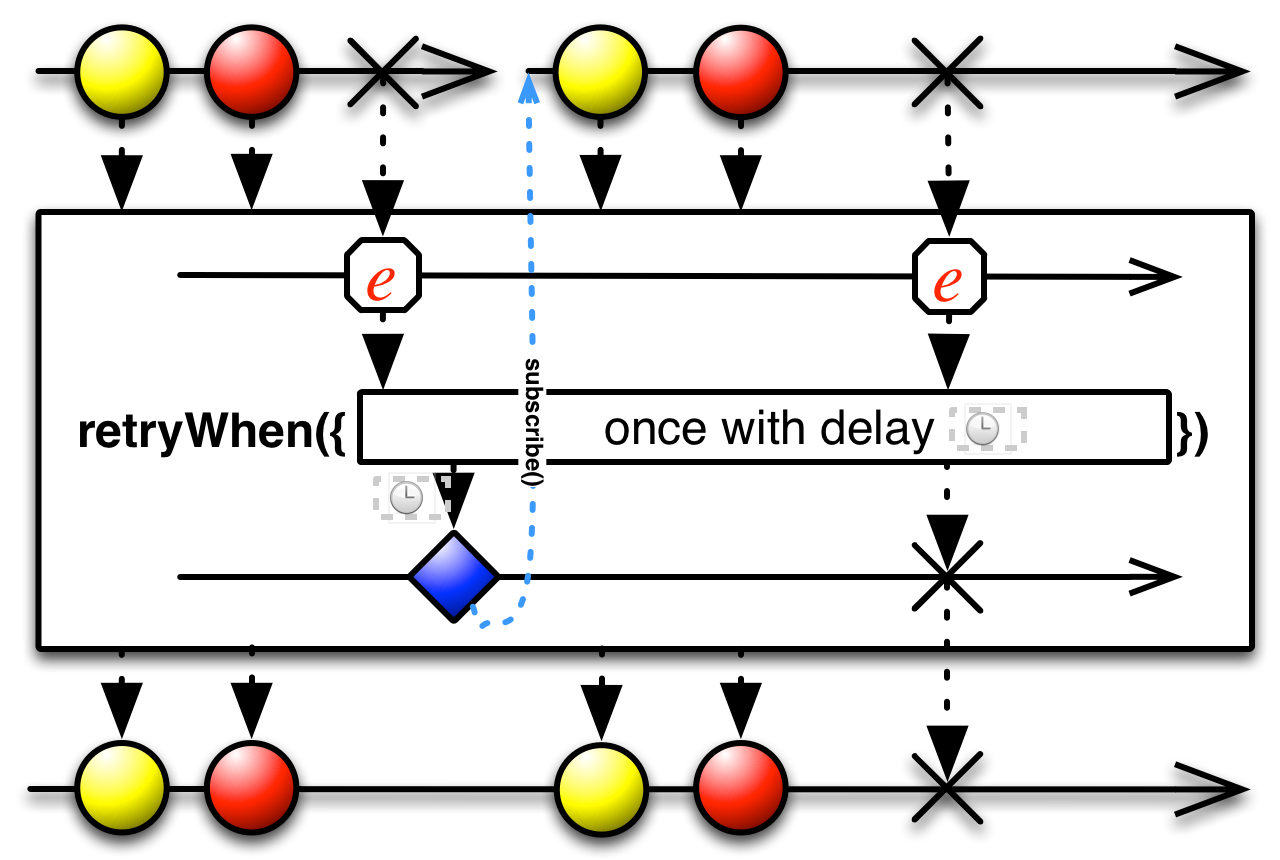
The retryWhen operator is similar to retry but decides whether or
not to resubscribe to and mirror the source Observable by passing the Throwable from the
onError notification to a function that generates a second Observable, and
observes its result to determine what to do. If that result is an emitted item,
retryWhen resubscribes to and mirrors the source and the process repeats; if
that result is an onError notification, retryWhen passes this
notification on to its observers and terminates.
retryWhen by default operates on the trampoline
Scheduler, and there is also a version that accepts a Scheduler as a
parameter.
retryWhen(Func1)retryWhen(Func1,Scheduler)
RxJava has two versions of this operator: retry and retryWhen.

One variant of retry takes no parameters. It will continue to resubscribe to and
mirror the source Observable no matter how many onError notifications it
receives.
Another variant of retry takes a single parameter: a count of the number of
times it should try to resubscribe to the source Observable when it encounters errors. If
this count is exceeded, retry will not attempt to resubscribe again and will
instead pass the latest onError notification to its observers.
A third variant of retry takes a predicate function as a parameter. You write
this function to accept two arguments: an Integer count of how many retries have taken place
thusfar, and a Throwable indicating the error that caused the onError
notification. This function returns a Boolean to indicate whether or not retry
should resubscribe to and mirror the source Observable. If it does not, then
retry passes the latest onError notification to its observers.
retry by default operates on the trampoline
Scheduler.
retry()retry(long)retry(Func2)
The retryWhen operator is similar to retry but decides whether or
not to resubscribe to and mirror the source Observable by passing the Throwable from the
onError notification to a function that generates a second Observable, and
observes its result to determine what to do. If that result is an emitted item,
retryWhen resubscribes to and mirrors the source and the process repeats; if that
result is an onError notification, retryWhen passes this
notification on to its observers and terminates.
retryWhen by default operates on the trampoline
Scheduler, and there is also a version that accepts a Scheduler as a
parameter.
Observable.create((Subscriber<? super String> s) -> {
System.out.println("subscribing");
s.onError(new RuntimeException("always fails"));
}).retryWhen(attempts -> {
return attempts.zipWith(Observable.range(1, 3), (n, i) -> i).flatMap(i -> {
System.out.println("delay retry by " + i + " second(s)");
return Observable.timer(i, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
});
}).toBlocking().forEach(System.out::println);subscribing delay retry by 1 second(s) subscribing delay retry by 2 second(s) subscribing delay retry by 3 second(s) subscribing
retryWhen(Func1)retryWhen(Func1,Scheduler)
RxJS implements this operator as retry.

One variant of retry takes no parameters. It will continue to resubscribe to and
mirror the source Observable no matter how many onError notifications it
receives.
Another variant of retry takes a single parameter: a count of the number of
onError notification it should be willing to accept before it too fails and
passes the onError to its observers. For example, retry(2) means
that retry will resubscribe to and mirror the source Observable the first time
it receives an onError notification, but will terminate with an error the second
time this happens.
retry is found in the following distributions:
rx.jsrx.all.jsrx.all.compat.jsrx.compat.jsrx.lite.jsrx.lite.compat.js
RxKotlin has two versions of this operator: retry and retryWhen.

One variant of retry takes no parameters. It will continue to resubscribe to and
mirror the source Observable no matter how many onError notifications it
receives.
Another variant of retry takes a single parameter: a count of the number of
times it should try to resubscribe to the source Observable when it encounters errors. If
this count is exceeded, retry will not attempt to resubscribe again and will
instead pass the latest onError notification to its observers.
A third variant of retry takes a predicate function as a parameter. You write
this function to accept two arguments: an Integer count of how many retries have taken place
thusfar, and a Throwable indicating the error that caused the onError
notification. This function returns a Boolean to indicate whether or not retry
should resubscribe to and mirror the source Observable. If it does not, then
retry passes the latest onError notification to its observers.

The retryWhen operator is similar to retry but decides whether or
not to resubscribe to and mirror the source Observable by passing the Throwable from the
onError notification to a function that generates a second Observable, and
observes its result to determine what to do. If that result is an emitted item,
retryWhen resubscribes to and mirrors the source and the process repeats; if
that result is an onError notification, retryWhen passes this
notification on to its observers and terminates.
Rx.NET implements this operator as Retry.

One variant of Retry takes no parameters. It will continue to resubscribe to and
mirror the source Observable no matter how many onError notifications it
receives.
Another variant of Retry takes a single parameter: a count of the number of
onError notification it should be willing to accept before it too fails and
passes the onError to its observers. For example, Retry(2) means
that Retry will resubscribe to and mirror the source Observable the first time
it receives an onError notification, but will terminate with an error the second
time this happens.
RxPHP implements this operator as retry.
Repeats the source observable sequence the specified number of times or until it successfully terminates. If the retry count is not specified, it retries indefinitely. Note if you encounter an error and want it to retry once, then you must use ->retry(2).
//from https://github.com/ReactiveX/RxPHP/blob/master/demo/retry/retry.php
$loop = \React\EventLoop\Factory::create();
$scheduler = new \Rx\Scheduler\EventLoopScheduler($loop);
$count = 0;
$observable = Rx\Observable::interval(1000, $scheduler)
->flatMap(function ($x) use (&$count) {
if (++$count < 2) {
return Rx\Observable::error(new \Exception("Something"));
}
return Rx\Observable::just(42);
})
->retry(3)
->take(1);
$observable->subscribe($stdoutObserver);
$loop->run();
Next value: 42
Complete!
RxPHP also has an operator retryWhen.
Repeats the source observable sequence on error when the notifier emits a next value. If the source observable errors and the notifier completes, it will complete the source sequence.
//from https://github.com/ReactiveX/RxPHP/blob/master/demo/retry/retryWhen.php
$loop = new \React\EventLoop\StreamSelectLoop();
$scheduler = new \Rx\Scheduler\EventLoopScheduler($loop);
$source = Rx\Observable::interval(1000)
->map(function ($n) {
if ($n === 2) {
throw new Exception();
}
return $n;
})
->retryWhen(function ($errors) {
return $errors->delay(200);
})
->take(6);
$subscription = $source->subscribe($createStdoutObserver(), $scheduler);
$loop->run();
// => Next: 0
// => Next: 1
// 200 ms pass
// => Next: 0
// => Next: 1
// 200 ms pass
// => Next: 0
// => Next: 1
// => Completed
Next value: 0
Next value: 1
Next value: 0
Next value: 1
Next value: 0
Next value: 1
Complete!
RxPY implements this operator as retry:

retry takes a single optional parameter, a count of the number of times it
should try resubscribing to and mirroring the source Observable when it encounters errors. If
this count is exceeded, retry will not attempt to resubscribe and will instead
pass the onError notification to its observers. If you omit this parameter,
retry will attempt to resubscribe and mirror indefinitely, no matter how many
onError notifications it receives.
Rx.rb has two versions of this operator: retry and retry_infinitely.

retry takes a single optional parameter, a count of the number of times it
should try resubscribing to and mirroring the source Observable when it encounters errors. If
this count is exceeded, retry will not attempt to resubscribe and will instead
pass the onError notification to its observers.
retryInfinitely, on the other hand, will attempt to resubscribe to and mirror the
source Observable indefinitely, no matter how many onError notifications it
receives.
RxScala has two versions of this operator: retry and retryWhen.

One variant of retry takes no parameters. It will continue to resubscribe to and
mirror the source Observable no matter how many onError notifications it
receives.
Another variant of retry takes a single parameter: a count of the number of
times it should try to resubscribe to the source Observable when it encounters errors. If
this count is exceeded, retry will not attempt to resubscribe again and will
instead pass the latest onError notification to its observers.
A third variant of retry takes a predicate function as a parameter. You write
this function to accept two arguments: an Int count of how many retries have taken place
thusfar, and a Throwable indicating the error that caused the onError
notification. This function returns a Boolean to indicate whether or not retry
should resubscribe to and mirror the source Observable. If it does not, then
retry passes the latest onError notification to its observers.

The retryWhen operator is similar to retry but decides whether or
not to resubscribe to and mirror the source Observable by passing the Throwable from the
onError notification to a function that generates a second Observable, and
observes its result to determine what to do. If that result is an emitted item,
retryWhen resubscribes to and mirrors the source and the process repeats; if
that result is an onError notification, retryWhen passes this
notification on to its observers and terminates.